In the world of medical device manufacturing, quality isn’t just a goal—it’s a system. ISO 13485 is the international standard that defines the requirements for a comprehensive Quality Management System (QMS). For any brand evaluating a manufacturing partner, understanding this standard is non-negotiable. This guide breaks down what ISO 13485 is, why it’s the cornerstone of medical device contract manufacturing, and what it means for the safety and success of your product.
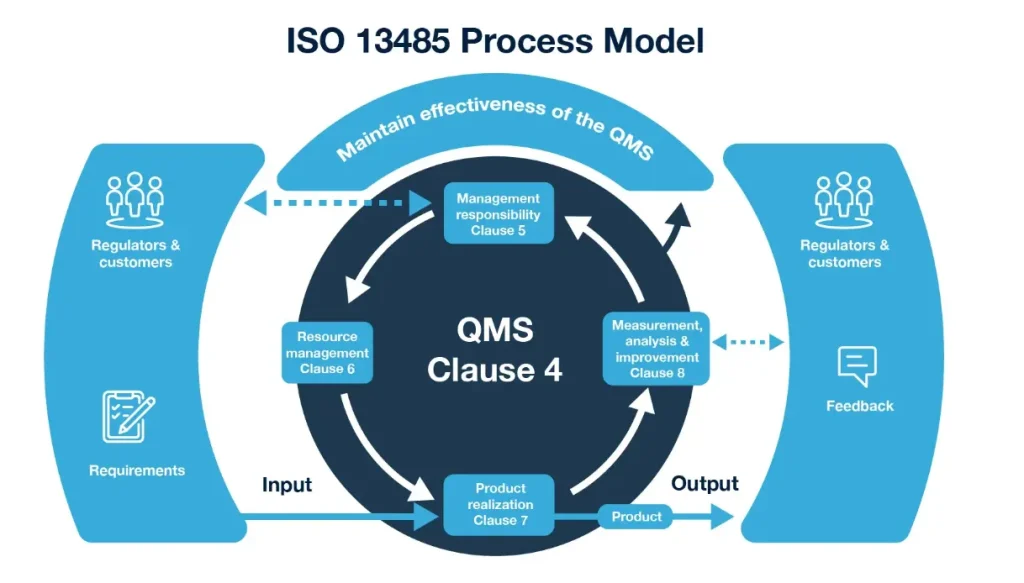
What is ISO 13485? Beyond a Certificate
ISO 13485 is more than a certificate on the wall; it’s a framework for consistent excellence. It specifies requirements for a QMS that enables an organization to consistently provide medical devices and related services that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Its focus is on the effective application of processes for the entire device life cycle, from design and development to production, storage, distribution, and post-market surveillance.
Core Pillars of the ISO 13485 Standard
The standard is built around several key principles that ensure a proactive, risk-based approach to quality:
- Document Control: Every process, specification, and procedure must be documented, approved, and controlled. This ensures consistency and provides a clear audit trail, which is essential for FDA registration and other regulatory submissions.
- Risk Management: Risk consideration is embedded throughout the entire product life cycle, from design to decommissioning. This aligns with the requirements of other regulations, making compliance more seamless.
- Process Validation: Critical processes, especially those whose outputs cannot be verified by subsequent monitoring or measurement (e.g., sterilization, sterile packaging sealing), must be validated to ensure they consistently achieve planned results.
- Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA): A robust system for addressing non-conformities, investigating root causes, and implementing actions to prevent recurrence is a central tenet of the standard.
ISO 13485 vs. ISO 9001: What’s the Difference for Medical Devices?
While both are quality standards, ISO 13485 is specifically tailored for the medical device industry. Key differences include:
- Stricter Regulatory Focus: ISO 13485 explicitly requires the QMS to meet regulatory requirements, making it the preferred standard for health authorities.
- Enhanced Traceability: Requirements for device identification and traceability are more rigorous.
- Focus on Risk: Risk management is a dedicated and pervasive requirement in ISO 13485, whereas in ISO 9001 it is one of several quality principles.
Why Your Contract Manufacturer Must Be ISO 13485 Certified
Choosing an ISO 13485 certified partner like Dinghmed is your greatest assurance of product quality and compliance. It means:
- Reduced Regulatory Risk: Our QMS is designed to meet the stringent requirements of global regulators, simplifying your own FDA registration and CE marking efforts.
- Consistent Product Quality: The standard ensures that every batch of product is manufactured with the same level of control and documentation, from raw materials to finished goods.
- A Partner in Quality: It demonstrates a fundamental commitment to quality that goes beyond simple inspection, building a foundation of trust for a long-term partnership.
Conclusion: The Foundation of Trust in Medical Manufacturing
ISO 13485 is the universal language of quality in the medical device industry. It is not an option but a prerequisite for any manufacturer claiming to produce safe and effective devices. By insisting on an ISO 13485 certified partner, you are investing in a foundation of quality that protects your brand, your customers, and your bottom line.
Partner with a manufacturer built on a foundation of quality. Contact Dinghmed to learn how our ISO 13485 certified QMS provides the assurance you need for your medical device project.
